Product monograph of Reshape Slim Powder
Introduction:
The term obesity is widely used and refers to an excess of total body fat. The causes of obesity are complex. At present it is the major health issue worldwide. On every continent of the globe, even in countries where malnutrition is widespread, the percent of the population that is either overweight or obese is increasing at an alarming rate.
The prevalence of obesity has been increasing due to a convergence of factors--the rise of TV viewing, our preference for take away and pre-prepared foods, the trend towards more computer-bound sedentary jobs, and fewer opportunities for sport and physical exercise.
Obesity and health:
The metabolic syndrome is a common metabolic disorder that results from the increasing prevalence of obesity. Obesity is an important determinant of cardiovascular disease (CVD). It is associated with a cluster of abnormalities according to American Heart Association obesity is a modifiable risk factor for the development of CVD. Obesity has a strong effect on lipoprotein metabolism. Overweight is a determinant of higher levels of triglycerides, elevated LDL-C, and low HDL-C, impaired glucose tolerance that together increase the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD
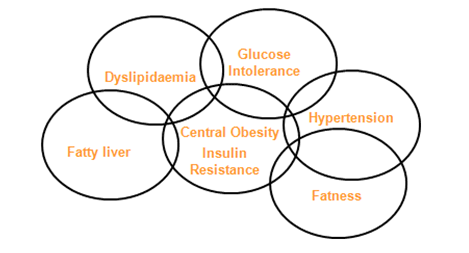
Hypertension:
Epidemiologic studies have consistently shown an association between obesity and blood pressure elevation.
High blood pressure has been identified as a major risk factor for stroke, congestive heart failure, renal disease and myocardial infarction. The risk of cardiovascular complications and organ damage in persons with high blood pressure is increased when other risk factors such as smoking, obesity, inappropriate dietary habits and physical inactivity are also present. In the opposite, the benefits from healthy dietary patterns on blood pressure control have been reported in several studies Therefore, appropriate nutrition related life-style modifications should be employed at all stages of high blood pressure managing.
Dyslipidemia:
Overweight and obesity are associated with the metabolic syndrome. Evidences indicate that greater deposition of central fat (abdominal/central obesity) is associated with less favorable plasma lipid and lipoprotein concentrations.
The most common pattern of lipoproteins seen in patients with obesity is elevation of plasma triglycerides (TG) and low HDL (high density lipoprotein) level.
Visceral adiposity has been associated with increased free fatty acids production via increased lipolysis of TG and from adipocytes in the intra-abdominal fat cells. The overproduction of very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) in obese individuals is probably a cause of this enhanced hepatic flux of free fatty acids. This may result in increased synthesis of triglyceride and LDL cholesterol in the liver. Also an increase in cholesterol synthesis in obese individuals provides a larger hepatic cholesterol pool which stimulates VLDL production
Adult Treatment Panel (ATP III) recommends a multifaceted lifestyle approach to reduce risk for cardiovascular diseases. This approach is designated therapeutic lifestyle changes (TLC) that primarily recommends: Reduced intakes of saturated fats & cholesterol, therapeutic options for enhancing LDL lowering such as plant stanols / sterols & weight reduction. (17 ATP III NCEP Guideline 2004)..
Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT):
Impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glucose represent two potentially reversible prediabetes conditions. Previous studies indicate that both conditions may be relatively common in obese individuals. The major factor driving the development of compromised glucose metabolism in obesity is severe insulin resistance. Severe obesity along with continued weight gain, specifically in obese youth, has been shown to be associated with deterioration of glucose tolerance over short periods of time. As obesity-related insulin resistance is associated with the development of altered glucose metabolism and other elements of the metabolic syndrome, severely obese youth are a high-risk group for the development of type 2 diabetes.
Obesity and reproductive health:
Obesity has a significant adverse impact on reproductive outcome. Fertility can be negatively affected by obesity. In women, early onset of obesity favours the development of menses irregularities, chronic oligo-anovulation and infertility in the adult age. Obesity in women can also increase risk of miscarriages and impair the outcomes of assisted reproductive technologies and pregnancy. The main factors implicated in the association may be insulin excess and insulin resistance. These adverse effects of obesity are specifically evident in polycystic ovary syndrome in women with upper body obesity and having higher androgen production rates and higher free testosterone.
In men, obesity is associated with low testosterone levels. In massively obese individuals, reduced spermatogenesis associated with severe hypotestosteronemia may favour infertility. Moreover, the frequency of erectile dysfunction increases with increasing body mass index.
Management of Obesity and Associated Risks:
Physical Exercise:
Overweight/obesity and physical inactivity are associated with a significantly higher risk of the metabolic syndrome along with smoking & intake of high-carbohydrate diet.
Several large randomized controlled trials provide strong evidence that favourable lifestyle changes, including regular physical activity, are effective in the prevention of diabetes mellitus (DM) in overweight patients and have impaired glucose tolerance. Physical exercise promotes the utilization of blood glucose and free fatty acids (FFA) in muscles and lowers blood glucose levels in well-controlled diabetic patients.
Epidemiological studies suggest that, in addition to DM, regular physical activity prevents cardiovascular disease (CVD) and premature mortality greatly. The Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) in the U.S. has shown the benefit of lifestyle intervention programs involving diet and/or in reducing the progression of impaired glucose tolerance (IGT).
Walking is the most common form of physical activity. It improves health in many ways and is generally safe. Therefore, brisk walking for at least 30 min daily can be recommended as the principal form of physical activity at the population level.
Regular physical activity 45-60 min per day prevents unhealthy weight gain and obesity. The best long-term results may be achieved when physical activity produces an energy expenditure of at least 2,500 kcal/week. Yet, the optimal approach in weight reduction programs appears to be a combination of regular physical activity and caloric restriction. A minimum of 60 min, but most likely 80-90 min of moderate-intensity physical activity per day may be needed to avoid or limit weight regain in formerly overweight or obese individuals.
Regular moderate intensity physical activity, a healthy diet, and avoiding unhealthy weight gain are effective and safe ways to prevent and treat cardiovascular diseases and to reduce premature mortality in all population groups.
Although the efforts to promote cardiovascular health concern the whole population, particular attention should be paid to individuals who are physically inactive, have unhealthy diets or are prone to weight gain.
Compliance with the current recommendations to increase the total volume of moderate-intensity physical activity and to maintain good cardiorespiratory and muscular fitness appears to markedly decrease the likelihood of developing the metabolic syndrome, especially in high-risk groups.
GOALS OF OBESITY MANAGEMENT:
- Successful 5-10% weight loss from baseline reduces health risk.
- Weight loss of approximately of 0.5 to 1 pound per week.
- Low-calorie diets for overweight and obese adults. An individually planned diet creating a deficit of 500 to 1000 kcal per day should be integral part of any program aimed to at achieving a weight loss of 1 to 2 lb per week.
- Physical activity- Accumulate at least 30 minutes or more of moderate-intensity physical activity on most, and preferably all days.
- Behavioural Therapy: Motivate patients to implement weight management, diet and physical exercise for achieving weight loss and maintenance.
RESHAPE SLIM
The healthy Way for Returning back to shape
Changes in lifestyle are considered to play an important role in the etiology of obesity and type 2 diabetes, and improvements in diet and physical activity are the first-choice. The treatment of obesity demands a negative energy balance, which obviously necessitates reducing the quantity of food intake. An optimum formula which not only provides the adequate vitamins and nutrients but also helps in weight reduction is the sole aim of any weight management program.
Optimum carbohydrate, higher fiber, lower fat provides and optimum vitamins and minerals ensure glycemic, lipidemic and weight management for long term in obese and overweight individual. Diabetologia. 2001;44(7):805-17
Hydroxycitric acid- A natural fat burner:
Hydroxycitric acid (HCA) is a principle constituent (10-30%) of the dried fruit rind of Garcinia cambogia, a plant native to Southeastern Asia. It is also known as natural fat burner. It is an herbal compound that purport to lower body weight.
Mechanism of action -
The primary mechanism of action of hydroxycitric acid appears to be related to its ability to act as a
competitive inhibitor of the enzyme ATP-citrate lyase, which catalyzes the conversion of citrate and coenzyme A to oxaloacetate and acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA), primary building blocks of fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis.
Hydroxycitric acid inhibits alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase, leading to reduction of carbohydrate metabolism
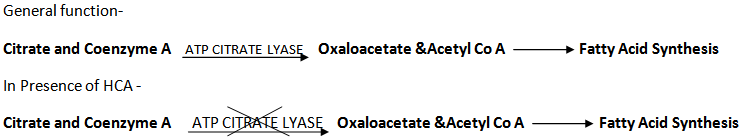
Clinical References -
- In a 8 weeks clinical trial in 60 human volunteers on 2,000 kcal diet/day, participated in a 30 min walking exercise program 5 days/week and 2,800 mg HCA at the end of therapy body weight and BMI decreased by 5.4% and 5.2%, respectively
- Significantly reduces the total cholesterol, LDL,triglycerides and serum leptin levels and increase the HDL and serum leptin level
- Highly effective adjunct to healthy weight control( (J Med 2004)
- In randomized controlled trial obese women supplemented with soluble calcium Garcinia for two months lost significantly more weight. This decrease in their body weight was evidenced by a significant decrease in the triceps skin fold thickness. It was concluded that HCA was an effective for weight management (Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2007; 16(1):25-9.)
Conjugated Linoleic acid (CLA):
The major sources of CLA in the human diet are meat and dairy products which are derived from grass fed ruminants
Mechanism Of action –
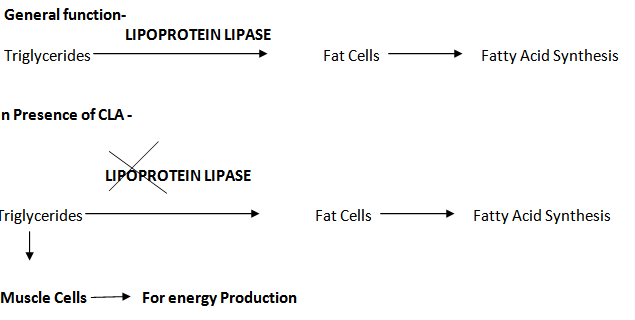
If fat consumed is not used for energy, the triglycerides are taken up by fat cells a mechanism for which the enzyme lipoprotein lipase is responsible.
CLA inhibits this enzyme, and instead the triglycerides are diverted to the muscle cells to be burnt. Here the CLA induces the activity of another enzyme, Carnitine palmitoyl transferase, which is responsible for oxidation and the burning of fat.CLA increases Lipolysis in adipocytes &enhances fatty acid oxidation in adipocytes & skeletal muscle cells & reduces fat. The preliminary studies on human and animal studies suggest that CLA can help control weight in obese individuals by reducing body fat and enhancing lean body mass
For energy Production
Clinical references
In 13 week duration interventional trial of overweight men and women on CLA supplementation, at the end of therapy the mean body weight loss was 6.9% from the baseline. Feelings of fullness and satiety were found to increase and feelings of hunger were decreased by CLA compared to placebo, independent of percentage body weight regain
(European Journal of Clinical of Nutrition. 2003; 57(10):1268-74)
Supplementation of CLA prevents abdominal fat mass and raises the fat free mass and adiponectin level
(Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008)
Conjugated Linoleic Acid(CLA) reduces the body fat in healthy exercising humans (J Int Med Res 2001).
Carbohydrates:
The high glycemic index carbohydrates increase blood sugars and stimulates fat production and inflammation, increases overall caloric intake and increase insulin resistance. Contrary to this low-carbohydrate intakes result in a reduction of the circulating insulin level, which promotes high level of circulating fatty acids, used for oxidation and production of ketone bodies. It is assumed that when carbohydrate availability is reduced in short term to a significant amount, the body will be stimulated to maximize fat oxidation for energy needs.( Obesity Reviews. 2006)
Fibers
Dietary fiber, also known as roughage or bulk, includes all parts of plant foods that your body can't digest or absorb. Unlike other food components such as fats, proteins or carbohydrates — which your body breaks down and absorbs — fiber isn't digested by your body. Therefore, it passes relatively intact through your stomach, small intestine, colon and out of your body. It might seem like fiber doesn't do much, but it has several important roles in maintaining health.
High-fiber foods generally require more chewing time, which gives your body time to register when you're no longer hungry, so you're less likely to overeat. Also, a high-fiber diet tends to make a meal feel larger and linger longer, so you stay full for a greater amount of time. And high-fiber diets also tend to be less "energy dense," which means they have fewer calories for the same volume of food. This acts as useful adjuvant in weight loss program .Apart from it also helps in control blood sugar level lowers blood cholesterol level which is also act as an added benefits of fibers. . The addition of functional fibers in weight loss therapy considered as tool to improve success. Dietary fiber: Essential for a healthy diet ,Mayoclinic Nov 19, 2009, Nutrition Vol 21,issue 3 March 2005
Calcium in regulation of body weight and associated risk:
Several observational studies have reported that dairy calcium significantly diminishes the post–prandial lipid response. According to human studies one possible mechanism is calcium has potential to increase fecal fat excretion which could be relevant for prevention of weigh (re-)gain. Obes Rev. 2009 Jul;10(4):475-86.
Vitamin D:
Human studies indicated that obese people tend to have lower levels of vitamin D than people who are not obese, and that supplementation may correct that deficiency. Obesity-associated vitamin D insufficiency is likely due to the decreased bioavailability of vitamin D3 from cutaneous and dietary sources because of its deposition in body fat compartments. (J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Jan;94(1):67-73. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000 Sep;72(3):690-3.)
A low vitamin D levels also reported to cause negative impact on β-cell function increase risk of insulin resistance and the metabolic syndrome. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;79(5):820-825
Chromium:
Chromium is an essential trace mineral required by the body for normal carbohydrate metabolism
Chromium enhances the biological action of insulin, the hormone that is critical for the normal regulation of carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism. Chromium helps insulin work more efficiently to allow blood sugar to move from the blood into the cells. J Am Coll Nutr 1998;17:548-555.
Chromium alongwith biotin was found to be an effective adjunctive nutritional therapy for people with poorly controlled diabetes with the potential for improving lipid metabolism. Acta Med Austriaca. 1997;24(5):185-7.
Protein- Whey Protein
Proteins are essential structural components of all cells and are needed by the body to build and repair tissues. Researchers reported that an increase in dietary protein from 15% to 30% of energy and a reduction in fat from 35% to 20%, at a constant carbohydrate intake, produce a sustained decrease in ad libitum calorie intake and results in significant weight loss. These results exhibited that protein is more satiating than is fat, and previous studies have shown that protein is more satiating than is carbohydrate. Am J Clin Nutr 2005;82:41–8, Physiol Behav 1988;43:145–53. J Am Diet Assoc. 2005 May;105(5 Suppl 1):S24-8.
Whey protein in compared to other food proteins contains higher concentration of branched chain amino acids especially leucine. It is easily digestable and improves leucine level which is important for muscle protein synthesis and anabolism.
Leucine is important for muscle cell protein synthesis during periods of restricted energy intake. It is involved in modulation of insulin signaling and utilization of glucose by skeletal muscle. Journal of the American College of Nutrition. 2007;26(6):704S-712S, Journal of Nutrition.2006; 136: 319S–323S
Dietary supplementation of branched-chain amino acid (5.76, 2.88 and 2.88 g per day of leucine, isoleucine and valine, respectively) significantly decreased (11.7%) fat mass. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1992;65(5):394-8.
In another study, administration of branched-chain amino acid (14 g/die; 50% L-Leucine, 25% L-Isoleucine, 25% L-Valine) for 30 days promoted fat free mass synthesis and improved physical fitness. Minerva Endocrinol. 1995 Dec;20(4):217-23.
B-vitamins:
Interventions which are aimed at weight control should maintain or improve nutritional status. Women supplemented with vitamin B6 increased pyridoxal phosphate level which could be helpful in maintaining fat-free mass during periods of weight loss. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008 Oct;32(10):1552-8
Obese and individuals are reported to have of b-vitamins deficiency which leads to increase in hyperhomocysteinemia (Hcy); increase risk of cardiovascular diseases. Indian Heart J. 2009 Mar-Apr;61(2):156-9.
Pantothenic acid (Vitamin B5) facilitates complete catabolism of fatty acids. As a result, a sufficient amount of energy -be released from storage fat to relieve the sensation of hunger and weakness. Med Hypotheses. 1995 May;44(5):403-5.
Multivitamin- Mineral Supplementation (MMS) in weight loss:
In a 26 weeks randomized placebo controlled trial on obese subjects effect of 29 ingredients containing multivitamin and mineral supplementation in obese women (n=96, Age: 18-55 yrs, BMI >28Kg/m2) was determined.
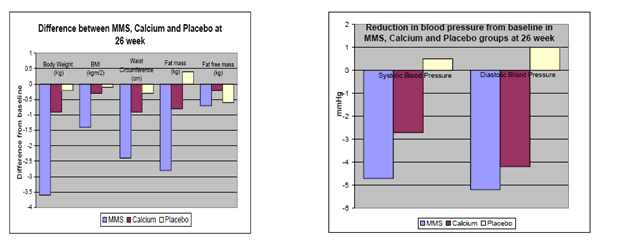
At the end of 26 weeks MMS found to reduce body weight, body mass index, and fatness and improved serum lipid profiles (total cholesterol, LDL-C) may be through increased energy expenditure and fat oxidation. While, women who were only on calcium (162 mg/d) demonstrated improvement only in lipid profile. Int J Obes (Lond). 2010 Jun;34(6):1070-7.
In 15 weeks energy restriction programme in consumers and non-consumer of vitamin or dietary supplementation was determined. It was observed that consumers who were on MMS reported reduction in lower body weight and fat. It was concluded that multivitamin mineral supplement during weight reduction programme seemed to have appetite related effect. Br J Nutr. 2008 May;99(5):1157-67
Reshape Slim is a combination of nutrients that have a positive synergistic effect in weight management. Reshape Slim ideal combination of essential vitamins and minerals along with natural fat burners which not only helps in reduce weight and its associated co morbidities but also it provides optimum nutritional formula which is very much essential in any weight loss program.
Reshape Slim offers following benefits
1. Low Calorie which is vital for weight loss Program
2. Provides Natural fat burners HCA (Hydroxy Citric Acid) and CLA (Conjugated Linoleic acid) which ensures optimum weight loss
3. Provides low glycemic profile ideal for Diabetic patients
4. Enriched with essential vitamins and minerals essential for weight loss
Reshape Slim product composition:-
. No |
Nutrient |
Per 100 g RESHAPE SLIM |
PER 30 G RESHAPE SLIM |
1 |
Carbohydrate |
53.6 g |
16.0 g |
2 |
Protein |
22.2 g |
6.7 g |
3 |
Fat |
2.90 g |
0.87 g |
4 |
Fiber |
7.0 g |
2.1 g |
5 |
Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) |
800 mg |
240 mg |
6 |
Hydroxycitric Acid (as Garcinia cambogia extract) |
600 mg |
180 mg |
|
VITAMINS |
|
|
7 |
Vitamin C |
240 mg |
72 mg |
8 |
Inositol |
240 mg |
72 mg |
9 |
Vitamin E |
120 mg |
36 mg |
10 |
Nicotinamide |
80 mg |
24 mg |
11 |
Pantothenic Acid |
40 mg |
12 mg |
12 |
Vitamin B6 |
8 mg |
2.4 mg |
13 |
Vitamin B1 |
6 mg |
1.8 mg |
14 |
Vitamin B2 |
6 mg |
1.8 mg |
15 |
Vitamin A (as Acetate) |
1800 mcg |
540 mcg |
16 |
Folic Acid |
1800 mcg |
540 mcg |
17 |
Biotin |
120 mcg |
36 mcg |
18 |
Vitamin D3 |
40 mcg |
12 mcg |
19 |
Vitamin B12 |
22 mcg |
6.6 mg |
|
MINERALS |
|
|
20 |
Chloride |
900 mg |
270 mg |
21 |
Potassium |
780 mg |
234 mg |
22 |
Calcium |
670 mg |
201 mg |
23 |
Phosphorous |
610 mg |
183 mg |
24 |
Magnesium |
400 mg |
120 mg |
25 |
Sodium |
330 mg |
99.0 mg |
26 |
Iron |
40 mg |
12 mg |
27 |
Zinc |
30 mg |
9 mg |
28 |
Manganese |
10 mg |
3 mg |
29 |
Copper |
3.0 mg |
0.9 mg |
30 |
Chromium |
400 mcg |
120 mcg |
31 |
Iodine |
300 mcg |
90 mcg |
32 |
Selenium |
240 mcg |
72 mcg |
33 |
Molybdenum |
100 mcg |
30 mcg |
34 |
Vanadium |
40 mcg |
12 mcg |
Benefits of Reshape Slim powder –
- Provides low Calories ideal for weight management.
- Natural Fat Burners ensures weight loss.
- Ensures optimum nutritional balance ideal for weight management
- Sugar Free ideal for Diabetic patients.
- High fiber contain ideal for weight loss
- Delicious Banana-Vanilla flavor
- As a dietary supplement in Obesity Management.
- As a Meal Replacement therapy
- Co-Prescription with Anti-Obesity drug for better results
- For Overweight and Obese with Co-Morbid condition...
- Ideal adjuvant in weight management Programme along with diet and exercise.
Conclusion
Obesity is a significant healthcare problem worldwide and increases the risk of developing debilitating including Type-2 Diabetes, Cardiovascular and other co-morbidities. Although the health benefits of weight reduction are well recognized, weight loss by diet and exercise fails in most of the patient. It is clear that there is a significant unmet need for overall approach in weight management
Reshape Slim it is an ideal supplement for weight loss and weight management control in patient with or without co-morbidities which not only helps in reducing weight but also provides optimum nutritional balance.
|